Understanding a Security Notification¶
Monitoring List subscribers receive notifications emails when new or updated relevant security notifications are published. A notifications email contains a summary of all notifications relevant for its receiver, grouped by affected monitoring lists. Each notification summary contains a link to the full version of the security notification available on the Vilocify Portal. In order to properly assess the possible impact of a security notification, it is vital to understand all information contained within. The following paragraphs describe the various parts of a typical security notification.
Title¶
The title of a security notification provides important information at a glance. Titles generally consists of three parts:
- Affected Systems: A summary of affected products and versions.
- Short Description: A summary of the vulnerability described within the notification
- Identifiers: Based on availability either an advisory or patch identifier, a vulnerability identifier or fixed versions
Example:

Overview¶
The overview is the first tab of a Vilocify notification, and it's purpose is to convey the most important attributes of a notification in a structured manner. It consists of several elements:
- Priority:
A rating that describes the severity of the information contained within a notification.
Factors like e.g. consequences of a successful exploitation, likelihood of exploitation and attack vector are considered when assigning a notification priority.
When available, a notification priority is based on the priority provided by the vendor, but the Vilocify team reserves the right to alter this according to their own analysis.
There are five possible ratings:
- Critical: Typically used for remote attacks with critical impact which cause full compromise of the system. Investigate immediately and follow recommended action as soon as possible with urgency.
- Major: Typically used for remote or local attacks with significant impact but no full compromise of system. Investigate as soon as possible and follow recommended action.
- Minor: Typically used for local attacks with minor impact to system. Follow the recommended action in a reasonable amount of time.
- Information Only: Typically used for notifications that are not directly related to vulnerabilities but could have a security impact nonetheless, e.g. updates of trusted root CAs or time zone information.
- Withdrawn: The vulnerability has been withdrawn by the vendor. It is no longer valid and can be disregarded.
- Action: Recommended action necessary to mitigate the issues described within the notification.
- Attack Vector: Describes where an attacker initiates an attack to exploit the vulnerabilities described in the notification.
- Vendor Affected components: A list of components that the vendor explicitly mentions as affected. It differs from the components in the Components tab as this list is provided directly by the vendor. Not all components mentioned in this section necessarily exist within the Vilocify Portal, as components in the Vilocify database are added only when explicitly requested through a component request.
- Solution: Indicates what type of solution is available. This value is derived from the corresponding CVSS metric (Remediation Level). It contains details about how to mitigate the vulnerabilities described in the security notification and might suggest to update to fixed versions, to apply patches provided by the vendor, to implement certain workarounds, etc. Vilocify follows a patch oriented approach, providing actionable information for a collection of vulnerabilities in one notification and would therefore also collect several vendor advisories to one notification, if they share the same solution.
- Description: Contains a detailed description of the vulnerabilities included in this notification. These descriptions are generally taken from the official vendor advisories, when available.
Example:

Components¶
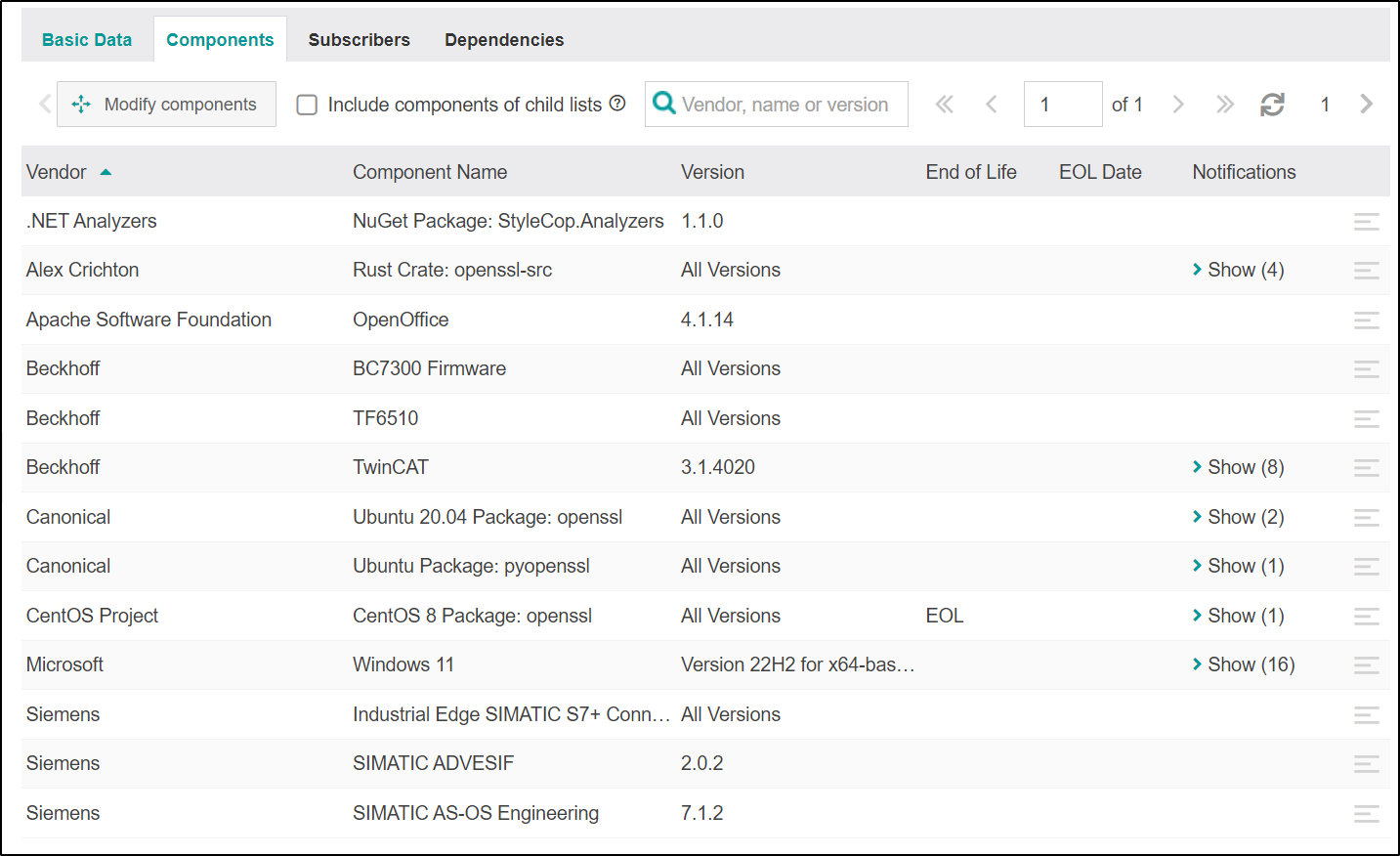
The next tab, "Components" contains a list of all Vilocify components assigned to this notification. If a user has a monitoring list containing one of the components in this section, this notification is relevant for him and will be included in his notifications email.
Example:
Vulnerabilities¶
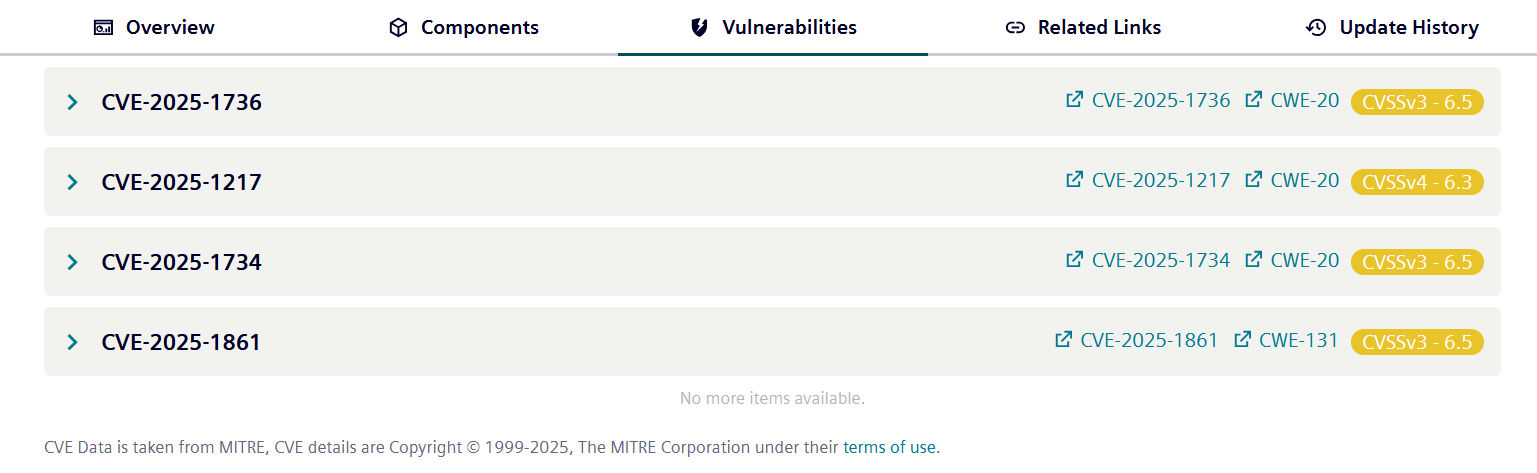
In the next tab "Vulnerabilities" as shown in the screenshot below, are all vulnerabilities listed for a certain notification. A vulnerability often contains a CVEs (Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures), which are identifiers assigned to specific vulnerabilities by so-called CVE Numbering Authorities. Vilocify publishes notifications for every CVE assigned by the Mitre Corporation, thus achieving CVE completeness. Not all vulnerabilities have assigned CVEs. Unlike the National Vulnerability Database by the NIST and many security information providers, Vilocify publishes notifications also for vulnerabilities without CVEs.
Example:
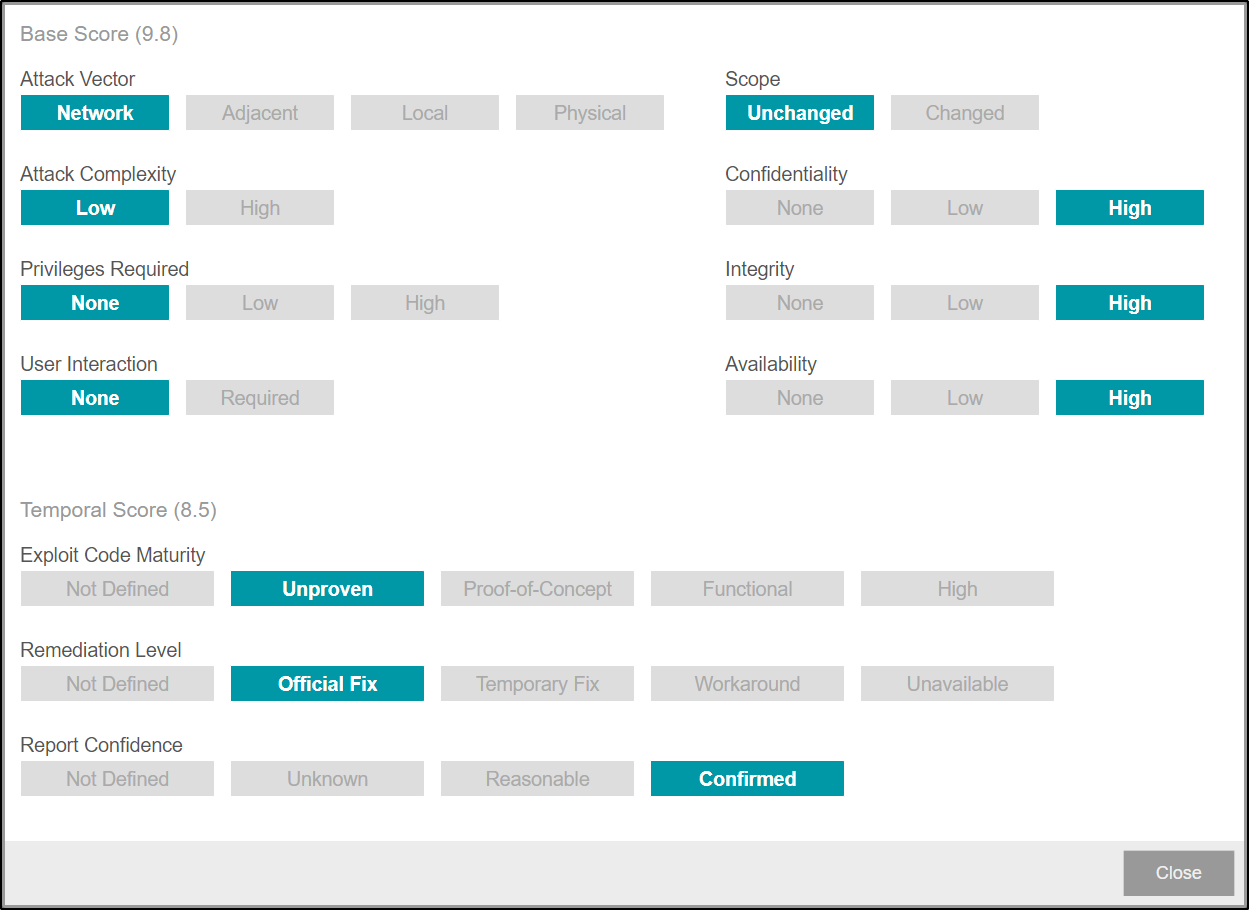
CVSS Score¶
The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) is a standard that allows to capture the most important metrics of a vulnerability in a structured manner, allowing to calculate a score reflecting its severity. Each Vilocify security notification has at least one CVSS vector for each reported vulnerability. Vilocify notifications support both CVSSv3.1 and CVSSv4.0 standards. The dual availability of CVSSv3.1 and CVSSv4.0 standards is part of a transition period from the end of October 2024 to the end of October 2025. During that transition period, Vilocify provides a CVSSv3.1 vector for every vulnerability that is scored with CVSSv4. After the transition period Vilocify only reports the CVSS version provided by the vendor, or CVSSv4 in the case where the vendor provides 3.1 and 4.
Note
Notifications published before 2017 are generally scored according to the CVSSv2 standard. Starting from October 2024, Vilocify will provide CVSSv4.0 scores whenever available.
The CVSS vectors of Vilocify vulnerabilities are determined in one of two ways:
- If the vendor provides its own CVSS score(s) in its vendor advisory or other official sources, Vilocify notifications report the provided score(s).
- In cases where the vendor does not provide any CVSS score, Vilocify will independently score the vulnerability(ies).
It is important to note that Vilocify does not rely on the scores provided by the NVD. Please see the FAQ for further information.
Vilocify does not provide the environmental metrics of a vulnerability, as it has no knowledge of all the differing environments a component is used in. Determining the correct environmental metrics (if needed) is the responsibility of each product manager or IT asset responsible.
There is not necessarily a correlation between notification priority and CVSS Base Score! The reason for this is that there are cases where CVSS does not address all necessary characteristics having an impact on the priority.
Example:
Extending a row in the vulnerability overview of a notification opens following visualization that explains the CVSS vector.
Related links¶
Vendor Advisory¶
A list of links to official advisories provided by the vendor. They often contain additional information.
References¶
A list of further resources that might contain additional information relevant to the vulnerabilities described in the notification.
CVEs¶
This section lists all CVEs assigned to the vulnerabilities within the security notification, if available.
Example:

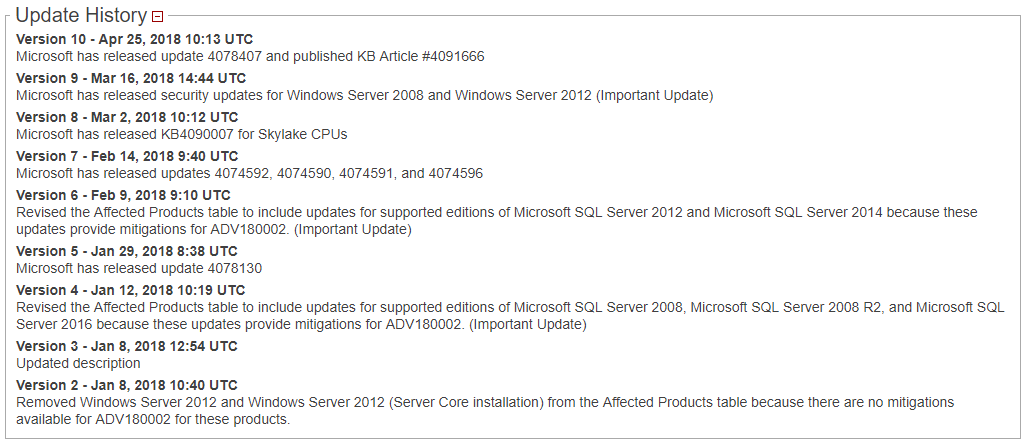
Update History¶
The information contained within a notification can be subject to change over time, e.g. the vendor might correct some mistakes made in previous versions of the advisory, security fixes could be provided only a certain time after the vulnerability is made public, etc. Vilocify security notifications are updated accordingly and changes are documented in this section. In case of important updates, a security notification is included again in the notifications email of affected users.
The following scenarios are considered as an important update:
- A new solution is available.
- The existing solution is changed due to a new patch, a new version or other similar reason.
- The priority of a notification increases due to e.g. a vulnerability being actively exploited.
- Official reports (from trusted sources) that a vulnerability is being actively exploited become available and thus the Exploit Code Maturity changes (e.g. FBI or CISA reports).
- New Vilocify affected component is added to the notification.
- The end of life date is rescheduled to an earlier point in time.
- New security impact is introduced when a vulnerability is added to a notification. e.g. a notification initially affects only Confidentiality and affects Availability with the addition of the new vulnerability.
The following scenarios are not considered as an important update:
- Updating description without new critical information.
- Adding new CVE without affecting the overall criticality and solution of the notification.
- Fixing spelling mistakes.
- Adding new reference links.
- Adding Nessus Plugins.
Example:
End-of-Life Notifications¶
Whenever possible, the Vilocify service generates End-of-Life notifications 18 months before a vendor stops supporting a specific component. In instances where such information is made available less than 18 months in advance, the time period can change accordingly. End-of-Life notifications are very similar to regular notifications, but lack some attributes like CVSS metrics, CVEs, Attack Vector, etc.
EOL information is provided on a "best effort" basis. This means publishing vulnerability notifications has priority and there is no guarantee that a EOL information can always be provided. The Vilocify service creates EOL notifications as far as they are known to it.